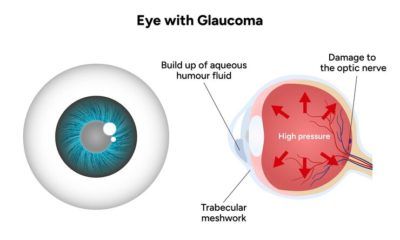
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of preventable blindness worldwide, yet many patients and families are unaware of how structured care can reduce risks. A personalised nursing care plan for glaucoma is essential to protect vision, reduce complications, and help patients adapt to lifestyle changes.
This guide explains the glaucoma care plan, common diagnoses, and step-by-step nursing management of glaucoma, offering practical information for patients, families, and caregivers.
Understanding Glaucoma and Its Impact on Vision
What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is an eye condition caused by damage to the optic nerve, usually due to increased intraocular pressure. If untreated, it can lead to permanent blindness. Effective glaucoma patient care focuses on controlling pressure and preventing further vision loss.
Types of Glaucoma
The two major types are chronic open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma. Open angle develops slowly, while acute angle closure presents with sudden pain and redness. A detailed nursing care plan for open-angle glaucoma differs from a nursing care plan for angle-closure glaucoma, as urgency and management vary significantly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Risk factors include genetics, blocked drainage channels, ageing, diabetes, prolonged corticosteroid use, and previous eye injuries. Nurses should assess these risks during care planning to create a targeted nursing diagnosis for glaucoma and prevent rapid progression.
Symptoms to Watch For
Glaucoma often progresses silently. Common symptoms include gradual loss of peripheral vision, blurred vision, halos around lights, eye pain, and headaches. Glaucoma nursing interventions for vision changes help patients adjust and seek timely medical care.
Why You Need a Nursing Care Plan for Glaucoma
Protecting Remaining Vision
The goal of any nursing care plan for glaucoma is to maintain current vision and slow down disease progression. Nurses monitor intraocular pressure, support medication compliance, and educate patients on protecting their visual field.
Supporting Patients Emotionally and Practically
Glaucoma can cause fear of blindness. Nurses provide emotional reassurance, guidance on daily activities, and assistance with medication schedules. This balance between emotional and practical support makes the glaucoma care plan comprehensive and patient-centred.
Goals of a Glaucoma Nursing Care Plan
Key goals include ensuring proper medication use, teaching self-care skills, and assisting patients in adapting to reduced vision. Nurses document progress, evaluate outcomes, and adjust interventions to strengthen the nursing care plan for glaucoma.
Common Nursing Diagnoses for Glaucoma Patients
Disturbed Sensory Perception (Visual)
Due to optic nerve damage and pressure, patients experience visual field loss. This nursing diagnosis for glaucoma requires interventions such as regular visual field assessments, environmental modifications, and emotional support to reduce frustration and improve safety.
Risk for Injury Related to Visual Limitations
Patients with reduced vision are prone to falls and accidents. Nurses modify the home setting, teach safety strategies, and encourage the use of assistive devices to support individuals with disabilities. Preventing injury is a crucial aspect of nursing management for glaucoma.
Knowledge Deficit About Disease and Treatment
Many patients struggle with complex medication regimens. Nurses educate them on correct eye drop techniques, side effects, and the importance. Addressing this nursing diagnosis for glaucoma prevents progression and reduces hospital readmissions.
Anxiety About Vision Loss and Procedures
Glaucoma can cause overwhelming anxiety. Nurses listen actively, provide reassurance, and guide patients about procedures. Emotional support is a cornerstone of the nursing care plan for glaucoma, improving compliance and quality of life.
Step-by-Step Nursing Interventions for Glaucoma
Preoperative Care and Teaching
Patients may undergo laser or surgical treatment. Nurses explain the use of eye drops, procedure expectations, and lifestyle adjustments. Preoperative teaching forms the base of effective nursing interventions for glaucoma to reduce anxiety and prepare patients.
Monitoring Intraocular Pressure and Visual Function
Regular monitoring of intraocular pressure and visual fields helps detect progression. Nurses educate patients on symptoms like sudden vision loss or eye pain, ensuring timely reporting for medical intervention.
Medication Management and Eye Drop Administration
Correct medication use is vital. Nurses demonstrate the proper technique for eye drop instillation, explain dosage timing, and discuss side effects. Effective nursing interventions for glaucoma medications enhance compliance and reduce complications.
Creating a Safe Home Environment
A safe home prevents accidents caused by poor vision. Nurses recommend bright lighting, clear walkways, handrails, and non-slip rugs to ensure a safe environment. These interventions are part of the nursing care plan for glaucoma, designed to support daily living.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies
Nurses encourage patients to share fears, connect with support groups, and practise relaxation exercises. Emotional support enhances resilience and facilitates patients’ adjustment to long-term disease management.
Sample Nursing Care Plan for Glaucoma
Example Diagnosis, Goals and Interventions
- Diagnosis: Disturbed sensory perception (visual).
- Goal: Maintain functional vision.
- Interventions: Monitor intraocular pressure, teach medication use, and modify the environment.
Expected Patient Outcomes
Patients achieve stable eye pressure, understand their treatment, and adapt safely to any changes in their vision. Clear outcomes are vital for evaluating any nursing care plan for glaucoma.
Documentation and Evaluation
Nurses must record all findings, patient responses, and modifications. Accurate documentation ensures the glaucoma care plan evolves to meet changing patient needs.
Counselling Patients and Families about Glaucoma Care
How to Use Eye Drops and Medicines
Nurses teach step-by-step eye drop techniques, emphasise hand hygiene, and highlight the importance of adherence. Correct use is central to nursing management of glaucoma.
Follow-Up Appointments and Regular Eye Exams
Routine check-ups are critical to track eye pressure and prevent progression. Missing appointments weakens the effectiveness of the nursing care plan for glaucoma.
Lifestyle and Diet Tips
Patients should manage their blood pressure, control diabetes, avoid smoking, and consume foods rich in antioxidants. Lifestyle changes complement the nursing management of glaucoma.
Recognising Warning Signs of Complications
Sudden eye pain, redness, or vision loss requires immediate medical help. Nurses empower patients and families to act quickly.
Home Nursing Care and Support Resources
Professional home nurses assist with medications, eye care, and daily activities. Support groups, vision rehabilitation programmes, and transport services reduce isolation and promote independence, enhancing the nursing care plan for glaucoma.
Prevention and Health Maintenance
H3: Regular Eye Check Ups for Early Detection
Adults over 40 and those with risk factors should undergo annual glaucoma screenings. Early detection improves outcomes and guides the nursing diagnosis for glaucoma.
Managing Health Conditions
Controlling systemic illnesses like diabetes and hypertension reduces the risk of worsening glaucoma. Nurses stress ongoing medical management as part of the nursing care plan for glaucoma.
Protective Eye Measures
Protective eyewear during risky activities and limiting UV exposure helps preserve vision. This advice supports long-term nursing management of glaucoma.
Conclusion
A structured nursing care plan for glaucoma is vital to prevent further vision loss and support patients emotionally and practically. By combining accurate nursing diagnosis for glaucoma, personalised interventions, and strong family involvement, the care plan improves outcomes and quality of life.