A lazy eye, also known as amblyopia, affects children and sometimes adults when one eye develops weaker vision due to poor coordination or differences in focusing. While early detection is critical, various lazy eye treatments, including eye exercises for lazy eyes, can improve visual outcomes.
These exercises are often combined with therapies such as patching, corrective lenses, or vision therapy. In this guide, we explain what lazy eye is, its causes, effective exercises, additional treatments, and when to seek medical help.
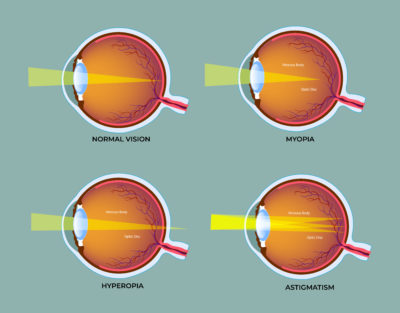
What Is Lazy Eye (Amblyopia)?
Lazy eye, medically called amblyopia, occurs when the brain favours one eye over the other, reducing vision in the weaker eye. It develops during childhood, often before the age of seven.
Unlike refractive errors corrected with glasses, amblyopia arises from the brain suppressing signals from the weaker eye. If left untreated, it may lead to permanent vision problems, but with early intervention and structured exercises, improvement is possible.
Causes of Lazy Eye
Strabismus (Misaligned Eyes)
Strabismus is when the eyes point in different directions, causing the brain to rely on the stronger eye. This leads to the suppression of the weaker eye and, eventually, amblyopia.
Refractive Errors
Large differences in refractive errors (short-sightedness, long-sightedness, or astigmatism) between the two eyes can cause the brain to rely more on the clearer eye, neglecting the other.
Deprivation Amblyopia
When visual development is blocked, such as by a congenital cataract or drooping eyelid, the brain cannot receive proper signals, leading to deprivation amblyopia, one of the most severe forms of visual impairment.
Eye Exercises for Lazy Eye
Pencil Push-ups Treatment (PPT)
This exercise involves focusing on a pencil held at arm’s length and gradually moving it closer to the nose while keeping it clear and single. It helps strengthen convergence ability.
Colouring Within the Lines
Encouraging children to colour pictures while wearing an eye patch over the stronger eye can improve focus, hand-eye coordination, and the use of the weaker eye in a structured way.
Brock String Exercise
A Brock string with beads is used to train both eyes to work together. Patients focus on different beads along the string, which strengthens binocular vision and depth perception.
Video Games for Lazy Eye
Certain video games, especially those designed for amblyopia therapy, stimulate both eyes and improve contrast sensitivity. This makes video games a modern and engaging treatment option for children.
Dot Card Exercise
Dot cards are printed with a row of dots. By focusing on these dots with both eyes, the exercise strengthens visual tracking and coordination between the eyes.
Barrel Convergence Cards
These cards display barrel-shaped images at increasing sizes. The patient focuses on each barrel from large to small, which improves convergence and binocular vision in lazy eye treatment.
Puzzles and Reading with an Eye Patch
Completing puzzles or reading with an eye patch on the stronger eye forces the weaker eye to develop focus, visual attention, and comprehension skills through consistent practice.
Benefits of Eye Exercises for Lazy Eye
Strengthening Eye Muscles
Exercises build strength in the weaker eye, improving control and reducing dependence on the stronger eye. This balance enhances overall eye muscle coordination.
Improving Coordination Between Eyes
Structured training helps both eyes work together. This helps reduce double vision and improve depth perception, which is crucial for daily activities such as sports and reading.
Enhancing Visual Function
Consistent eye exercises for lazy eye can enhance clarity, focus, and brain-eye coordination. This results in improved visual function and a reduction in the long-term complications of amblyopia.
Other Treatments for Lazy Eye
Vision Therapy
Structured programmes by eye specialists combine eye exercises for lazy eye, lenses, and prisms to retrain the brain and improve eye coordination.
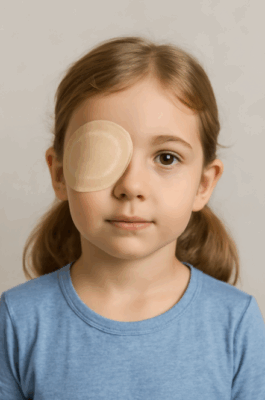
Eye Patching
Wearing an eye patch on the stronger eye forces the weaker eye to work harder, strengthening neural connections and vision.
Corrective Eyewear
Prescription glasses or contact lenses address underlying refractive errors, ensuring both eyes receive clear images for balanced vision.
Eye Drops for Blurring Vision
Special atropine eye drops blur the stronger eye, forcing the weaker one to be used more, an alternative to eye patching in children.
Surgery for Lazy Eye
In cases of strabismus or structural problems, surgery can help align the eyes. This allows the eyes to work together more effectively, enhancing the benefits of exercises and therapy.
When to See a Doctor for Lazy Eye?
Seek professional evaluation if a child has persistent eye misalignment, blurred vision in one eye, or noticeable lack of coordination. Early intervention before age seven provides the best outcomes, but adults may also benefit from treatment.