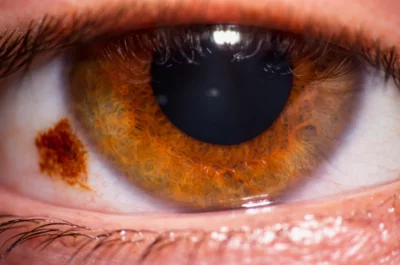
Cholesterol deposits around the eyes, also known as xanthelasma, often appear as soft, yellowish patches on or near the eyelids. While these deposits are usually painless, they can affect appearance and sometimes signal underlying health conditions such as high cholesterol, thyroid problems, or diabetes.
Many people search for natural ways to manage them, but it’s equally important to understand medical treatments and long-term prevention. This article explains the causes, risk factors, natural remedies, and medical treatments for xanthelasma, as well as prevention tips and when to seek professional care.
What is Xanthelasma?
Xanthelasma refers to fatty, yellowish deposits that develop under the skin around the eyelids. These are caused by the build-up of cholesterol and other lipids in the skin’s cells.
While not cancerous or directly harmful, they can indicate elevated blood cholesterol levels and an increased risk of heart disease. Xanthelasma can affect both upper and lower eyelids and may appear symmetrically on both eyes.

Causes of Cholesterol Deposits Around the Eyes
Understanding the causes of cholesterol deposits around the eyes is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
High Cholesterol Levels
Excess cholesterol circulating in the bloodstream is one of the leading causes of cholesterol deposits around the eyes. When cholesterol levels remain high over time, fatty substances may accumulate in different parts of the body, including the eyelids.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar
People with diabetes often struggle with imbalanced lipid metabolism. Poorly controlled blood sugar can lead to higher triglyceride and cholesterol levels, increasing the likelihood of xanthelasma formation.
Thyroid Issues
Thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism, can contribute to lipid abnormalities. Reduced thyroid activity may raise low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which in turn increases the risk of developing deposits near the eyes.
Poor Lifestyle Habits
A diet high in processed foods, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen lipid levels and promote the development of fatty deposits in the eyelids.
Genetics and Family History
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role. Even with healthy habits, some individuals may develop xanthelasma due to inherited conditions such as familial hypercholesterolaemia.
Risk Factors for Cholesterol Deposits
Certain groups are more likely to develop xanthelasma due to the combined effects of health and lifestyle factors.
High Cholesterol Levels
Persistently high LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and triglyceride levels remain the strongest risk factor for xanthelasma.
Diabetes and Thyroid Issues
Endocrine disorders like diabetes and thyroid disease significantly increase risk. These conditions interfere with the body’s ability to process fats efficiently, resulting in lipid deposits.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, alcohol intake, poor diet, and lack of exercise are eye swelling reasons that not only affect general health but also make cholesterol deposits around the eyes more likely to occur.
How to Treat Cholesterol Deposits Around Eyes Naturally
While medical treatments provide faster results, some people prefer trying natural remedies for xanthelasma. Evidence is limited, but certain methods may help reduce or control cholesterol deposits.
Garlic Therapy
Garlic therapy is often suggested because garlic has natural lipid-lowering and anti-inflammatory properties. Crushed garlic can be applied to the deposit for a few minutes daily, but care must be taken to avoid skin burns.
Banana Peel Remedy
Applying a banana peel to the affected area may reduce the appearance of xanthelasma. Its natural antioxidants and enzymes are believed to support skin health and help break down deposits gradually.
Fenugreek Seeds
Soaking fenugreek seeds overnight and applying the paste to the cholesterol bump on the eyelid has been a traditional remedy. Fenugreek may help lower cholesterol levels internally and improve lipid metabolism.
Onion Consumption
Onions are rich in antioxidants and compounds that help regulate cholesterol. Some xanthelasma home remedies suggest applying onion juice directly to the eyelids, but this can irritate. Consuming onions regularly is a safer option.
Medical Treatments for Xanthelasma
If natural approaches are ineffective, several medical options are available to treat cholesterol deposits around the eyes.
Surgical Removal
A small surgical excision under local anaesthetic can quickly remove xanthelasma. This is effective but carries a risk of scarring.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy, especially CO₂ or Er: YAG lasers, targets and vaporises cholesterol spots on the eyes with precision. It offers good cosmetic results and minimal scarring when performed by an experienced doctor.
Cauterization Methods
Electro-cautery or chemical cauterization can be used to burn off deposits. These are usually considered for smaller lesions and may require repeat sessions.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
Long-term management of cholesterol deposits requires lifestyle changes to control underlying risk factors.
Lifestyle Changes
Avoid smoking, limit alcohol intake, and incorporate daily physical activity. Regular exercise helps reduce bad cholesterol and raise protective high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels.
Diet Adjustments
Adopt a diet rich in leafy greens, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids from fish or nuts. Reduce intake of processed foods, red meat, and trans fats.
Regular Checkups
Routine cholesterol testing and eye checkups are vital for monitoring lipid levels and eye health. Early detection of changes can prevent recurrence of xanthelasma and help manage cardiovascular risk.
When to See a Doctor for Xanthelasma
While xanthelasma home remedies may offer some relief, professional care ensures a proper diagnosis and effective treatment.
Persistent Bumps
If stubborn cholesterol bumps under the eyes remain despite lifestyle changes or natural remedies, consult an ophthalmologist or dermatologist for evaluation.
Recurrence After Treatment
Xanthelasma often reappears after removal. Recurrence, particularly with worsening cholesterol or other health issues, requires a thorough medical checkup and long-term lipid management.