Corneal topography is an essential diagnostic tool in modern ophthalmology, providing detailed maps of the cornea’s curvature and surface. One of the most widely used methods for this purpose is the Placido disc system, which has become the foundation for accurate and non-invasive corneal imaging.
By reflecting concentric rings on the cornea and analysing distortions, it offers valuable insights into eye health, aiding in the detection of abnormalities and supporting treatment planning.
What is Corneal Topography?
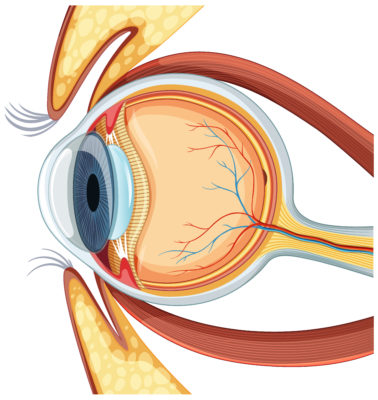
Corneal topography is a non-invasive imaging technique used to create a three-dimensional map of the cornea. This map helps assess curvature, symmetry, and irregularities on the corneal surface.
It plays a crucial role in diagnosing corneal diseases, monitoring changes, and preparing for refractive surgeries such as LASIK surgery. Ophthalmologists also rely on it for contact lens fitting, ensuring precise measurements for optimal comfort and vision correction.
How Does Corneal Topography Work?
The process involves projecting a series of rings or grids onto the cornea. The reflection patterns are captured by a camera and processed using software to calculate curvature and variations in shape.
The resulting map displays different colours representing steep, flat, or irregular areas. By comparing these maps, eye specialists can detect conditions such as keratoconus, astigmatism, and corneal thinning. It provides both qualitative and quantitative data essential for personalised treatment plans.
Placido Disc: The Key to Accurate Corneal Mapping
How Placido Disc Topography Works
The Placido disc method uses concentric rings projected onto the corneal surface. The reflection pattern indicates surface curvature, with distortions suggesting irregularities. By analysing these reflections, the software generates a detailed corneal map.
This technique has been a cornerstone in clinical practice due to its precision in detecting subtle changes. It is particularly effective for identifying early keratoconus and evaluating post-surgical outcomes.
Benefits of Using the Placido Disc
Placido disc topography provides high-resolution images of corneal curvature, making it invaluable for both diagnosis and surgical planning. Its non-invasive nature ensures patient comfort, while its speed makes it suitable for routine practice.
It also detects small irregularities that may not be visible in standard eye exams, enabling early treatment. Compared to manual methods, Placido-based imaging offers superior accuracy and consistency.
Types of Corneal Mapping and Their Significance
Axial Display Map
The axial map displays the average curvature of the cornea relative to its visual axis. It provides an overall view of corneal shape, making it useful for routine assessments and identifying generalised irregularities.
Tangential Demonstration Map
Tangential maps offer more localised detail compared to axial maps. They highlight small irregularities in curvature, making them particularly useful in detecting early keratoconus or post-surgical ectasia.
Elevation Map
An elevation map compares the cornea’s shape to a reference sphere or ellipsoid. It identifies raised or depressed areas, helping in the diagnosis of ectatic conditions and for surgical planning.
Corneal Thickness Map
Also called pachymetry maps, these measure corneal thickness across the surface. They are essential in screening patients for refractive surgery and monitoring corneal diseases like keratoconus or corneal oedema.
Tear Break Up Time Map
This map evaluates tear film stability. Analysing how the tear layer breaks up after blinking provides insights into dry eye syndrome and helps guide treatment for ocular surface disorders.
Purpose and Applications of Corneal Mapping
Diagnosing and Monitoring Eye Conditions
Corneal topography is critical for diagnosing disorders such as keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration, and corneal scarring. It also tracks disease progression and evaluates the success of interventions, ensuring accurate monitoring over time.
Contact Lens Fitting and Prescription
Precise corneal measurements allow customised contact lens fitting. For patients with irregular corneas, topography ensures better comfort, stability, and vision correction compared to standard fitting techniques.
Pre-Surgical Assessment for Laser Vision Correction
Before LASIK or PRK, corneal mapping ensures the cornea is strong and regular enough for surgery. It helps determine surgical eligibility, plan treatment patterns, and reduce risks of post-surgical complications.
Advantages of Placido Disc and Corneal Topography
Non-Invasive and Detailed Corneal Mapping
Placido disc topography is entirely non-invasive, requiring no direct contact with the eye. It provides detailed curvature maps within seconds, improving efficiency while maintaining patient safety and comfort during routine assessments.
Early Detection of Corneal Abnormalities
The high sensitivity of Placido-based imaging enables the detection of early corneal abnormalities, such as subclinical keratoconus. This early recognition allows timely interventions, preventing disease progression and reducing the risk of vision loss.
Placido Disc vs. Corneal Tomography: Key Differences
Which One is Best for Your Needs?
While Placido disc topography focuses on anterior surface curvature, corneal tomography provides three-dimensional imaging, including posterior surface and corneal thickness. Tomography offers more comprehensive data but is costlier and less widely available.
Placido topography remains a reliable choice for routine clinical practice, while tomography is preferable in complex or surgical cases. The choice depends on clinical requirements and the patient’s condition.
Common Conditions Detected Through Corneal Topography
Keratoconus
Keratoconus causes thinning and bulging of the cornea. Placido disc topography detects early irregularities, helping initiate treatments such as corneal cross-linking before vision loss becomes significant.
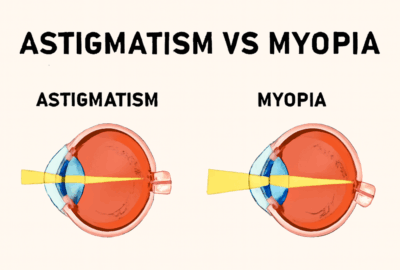
Astigmatism
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea is unevenly curved. Topography maps reveal the degree and orientation of distortion, aiding in the accurate prescription of glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery planning.
Post-Refractive Surgery Ectasia
Some patients may develop corneal weakening after LASIK or PRK. Topography identifies early signs of ectasia, allowing timely management with cross-linking or customised lenses.
Corneal Scarring
Scars from trauma or infection cause irregular corneal surfaces. Topography maps highlight the impact of scarring on curvature, guiding treatment decisions such as keratoplasty or lens fitting.
Dry Eye Syndrome
Irregular tear film distribution can affect corneal imaging. Tear break-up maps detect dry eye syndrome, enabling targeted treatments with lubricants, punctal plugs, or lifestyle adjustments.
Pellucid Marginal Degeneration
This rare condition causes thinning of the lower cornea. Topography reveals characteristic inferior steepening, which helps distinguish it from keratoconus and guides management.
Terrien Marginal Degeneration
A rare thinning disorder affecting the corneal periphery, Terrien marginal degeneration is best identified through detailed corneal maps, allowing early detection and management to reduce complications.
Conclusion
The Placido disc remains a cornerstone in corneal topography, offering accurate, non-invasive mapping of corneal curvature. While tomography provides broader insights,
Placido imaging continues to be essential for diagnosing conditions, fitting lenses, and surgical planning.
Its ability to detect early abnormalities ensures better outcomes and supports long-term eye health. For patients and clinicians, understanding its role highlights why corneal topography is a critical tool in modern ophthalmology.