Vision problems are among the most common eye conditions worldwide, often affecting people from a young age. Two terms frequently encountered in eye health are astigmatism and myopia. While both impact how clearly a person can see, their underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches differ significantly.
Many people search for clarity on astigmatism vs myopia to better understand their diagnosis and treatment options. This guide explains what astigmatism is, what myopia is, and the key differences between these conditions, helping you make informed decisions about your eye health.
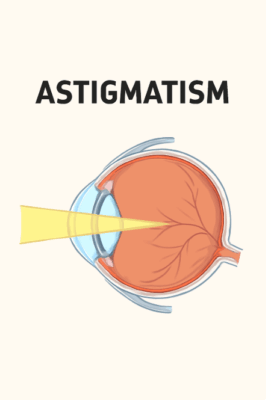
What is Astigmatism?
To begin with, the meaning of astigmatism is that it is a common refractive error where the cornea or lens has an irregular curve. Instead of being round like a basketball, the cornea is shaped more like a rugby ball.
This uneven curvature bends light unevenly, causing blurred or distorted vision at all distances. Astigmatism can occur alongside other refractive errors, such as myopia or hyperopia, and may require specific corrective lenses.
What is Myopia?
Myopia, also known as short-sightedness, is a condition where nearby objects are seen clearly, but distant objects appear blurry.
This happens when the eyeball is too long or the cornea is too curved, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. Myopia is one of the most common vision conditions globally, often starting in childhood and progressing through teenage years.
Astigmatism vs Myopia: Key Differences
Although both conditions affect vision, the distinction between astigmatism and myopia lies in their causes, symptoms, and management.
Causes
Astigmatism is caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, while myopia results from an elongated eyeball or overly curved cornea. Genetics and environmental factors can influence both conditions.
Symptoms
Astigmatism often leads to distorted or blurred vision at all distances, headaches, and eye strain. Myopia mainly causes distant objects to appear blurry, with squinting and eye fatigue as common complaints.
Appearance
Astigmatism does not change the appearance of the eye. In contrast, high levels of myopia may cause visible elongation of the eyeball, sometimes noticeable in severe cases.
Nature of the Condition
Astigmatism is characterised by uneven light refraction in multiple directions. Myopia is a condition in which light focuses too far forward, specifically affecting distance vision.
Risk Factors
Family history increases the risk of both conditions. Astigmatism may result from eye surgery or trauma, whereas the risk of myopia rises with prolonged near work, limited outdoor activities, and genetic predisposition.
Diagnosis
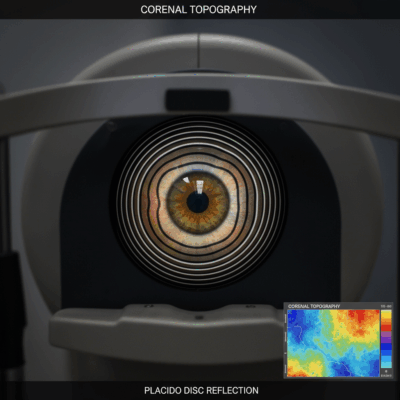
Both conditions are diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination. Astigmatism requires keratometry or corneal topography to measure corneal curvature, while myopia is usually confirmed through visual acuity and refraction tests.
Treatments
Astigmatism is treated with toric lenses, glasses, or refractive surgery like LASIK. Myopia is corrected with single-vision lenses, contact lenses, or surgical procedures such as LASIK or Contoura Vision.
Prevention
Astigmatism cannot be prevented, but progression can be managed. Myopia prevention strategies include spending more time outdoors, limiting prolonged screen use, and regular eye check-ups during childhood to track progression.
When to See a Doctor for Astigmatism or Myopia
You should consult an eye specialist if you experience persistent blurred vision, frequent headaches, squinting, or difficulty seeing objects at specific distances. Regular eye tests are essential to detect changes in prescription and to monitor overall eye health. If you have a family history of myopia or astigmatism, early detection helps in timely correction and management.
Conclusion
In summary, while both conditions affect vision, the distinction between astigmatism and myopia is clear. Astigmatism results from irregular curvatur, causing distorted vision at all distances, whereas myopia specifically affects distance vision due to an elongated eyeball.
Understanding what astigmatism is and what myopia is allows patients to recognise symptoms, seek timely diagnosis, and pursue suitable treatments such as corrective lenses or refractive surgery. Regular eye check-ups remain the most effective way to maintain healthy vision.