A retinal hemorrhage is a serious eye condition in which bleeding occurs within the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that forms clear images. When blood vessels in the retina break or leak, vision can become blurred or distorted.
In severe cases, untreated bleeding may lead to permanent vision loss. Understanding the causes, types, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for timely medical care and long-term protection of sight.
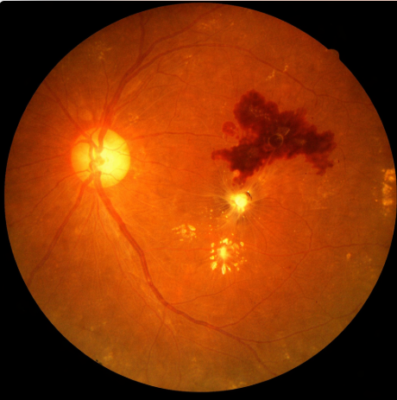
What Is Retinal Hemorrhage or Retinal Bleeding?
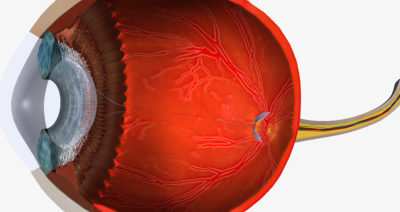
A retinal hemorrhage refers to the leakage of blood into the retinal tissue due to damaged or fragile retinal blood vessels. This condition is often described as retinal bleeding, and it can affect anyone, though it is more common among individuals with systemic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension.
The presence of blood within the retina can interfere with normal vision, depending on the location and severity of the hemorrhage. Early diagnosis is critical to prevent complications and preserve vision.
Types of Retinal Hemorrhage
Different types of retinal hemorrhage affect vision in distinct ways. The most common include:
- Superficial Retinal Hemorrhages: These occur in the nerve fibre layer and appear as flame-shaped streaks. They are often linked to hypertension or vascular diseases.
- Deep Retinal hemorrhages: Located in the deeper retinal layers, these appear as dot- and blot-shaped spots. They commonly occur in diabetic retinopathy.
- Preretinal hemorrhages: These accumulate between the retina and the vitreous. Because they sit closer to the visual axis, they can significantly impact vision.
The type and location of the hemorrhage help ophthalmologists determine the underlying cause and the appropriate management plan.
Symptoms of Retinal Hemorrhage
Common retinal hemorrhage symptoms to watch for include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Sudden appearance of floaters
- Dark spots, cobweb-like shadows, or blind patches
- Reduced ability to see fine details
- Sudden vision loss in severe cases
Common Causes of Retinal Hemorrhage
Multiple conditions can cause or contribute to retinal bleeding. Key retinal hemorrhage causes include:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: High blood sugar damages the small retinal blood vessels, causing them to leak or bleed.
- Hypertension: Uncontrolled high blood pressure weakens blood vessel walls, leading to ruptures.
- Trauma: A direct hit to the eye or head injury can cause immediate retinal bleeding.
- Vascular Disorders: Diseases affecting blood circulation, such as retinal vein occlusion, can trigger hemorrhages.
- Autoimmune or Blood Disorders: Conditions affecting clotting or causing vessel inflammation can also increase the risk.
Identifying and treating the underlying systemic condition is essential for preventing recurrence.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Retinal Hemorrhage
Accurate diagnosis guides effective retinal hemorrhage treatment. Ophthalmologists use several diagnostic tools to assess the extent of bleeding and retinal damage:
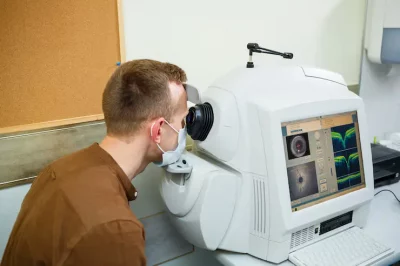
- Fundoscopy: A detailed examination of the retina using a specialised lens and light source.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): A non-invasive imaging technique that provides cross-sectional images of the retina to detect fluid or structural changes.
- Fluorescein Angiography: A dye-based test that helps evaluate blood vessel leaks or blockages.
Treatment Options
Treatment for retinal hemorrhage varies depending on the cause and severity:
- Laser Therapy: Used to seal leaking blood vessels or reduce abnormal growth in diabetic retinopathy.
- Anti-VEGF Injections: Medications that block abnormal vessel growth and reduce leakage.
- Vitrectomy Surgery: A procedure to remove blood from the vitreous cavity in severe or non-resolving cases.
- Systemic Disease Management: Controlling diabetes, hypertension, or clotting disorders to prevent further damage.
How to Prevent Retinal Hemorrhage
Although not all retinal hemorrhages are preventable, following key precautions can reduce risk:
- Keep blood sugar levels within the target range
- Manage high blood pressure with regular medication and monitoring
- Attend routine eye check-ups, especially if diabetic or hypertensive
- Avoid eye trauma by using protective eyewear during sports or high-risk work
- Manage cholesterol and vascular health
- Stop smoking, as it impairs circulation and retinal health
When to See A Doctor for Retinal Hemorrhage or Retinal Bleeding?
Retinal hemorrhage is a serious condition where immediate medical attention is critical to protect your sight. The fundamental goal in managing this condition is early detection of symptoms, leading to proper treatment, and ultimately, prevention of recurrence.
The symptoms you need to look for include sudden vision loss, severe blurring, the appearance of new or worsening floaters, dark shadows, or persistent visual distortion. These are ophthalmologic emergencies and should prompt an immediate visit to an eye care specialist.
It is important to remember that delaying diagnosis and treatment can lead to irreversible damage. This is why managing underlying causes, such as strict control of diabetes and hypertension, along with regular comprehensive eye check-ups, is essential for long-term vision preservation.