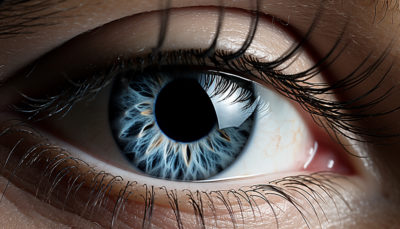
What Is Keratoconus?
Keratoconus is a condition of the eye in which the normally round cornea becomes thin and bulging like a cone.
What are the symptoms of Keratoconus?
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Light Sensitivity
- Multiple images
- Eye strain
- ‘Ghost images’-Appearance like several images when looking at one object
What are the causes of Keratoconus?
The cause for Keratoconus is unknown. It usually starts in the late teens to early twenties and may continue for several years.
What is the treatment for Keratoconus?
Several treatments are available today for keratoconus but depending on the severity of keratoconus the treatment is opted. The treatments include:
- Corneal Cross Linking (CXL): Also known as Corneal Collagen Cross Linking .It strengthens the corneal tissue to halt bulging of the eye’s surface in Keratoconus cornea.
- Gas permeable contact lenses: These are a kind of contact lenses that are rigid gas permeable that are placed over the cornea thereby replacing its irregular shape with a smooth, uniform surface for better refraction that improves vision. This will help correct vision as keratoconus progresses.
- Intacs: Intacs are inserted into the mid layer of the cornea to flatten it. This changes the shape and location of the cone.
- Topography guided conductive keratoplasty: This treatment uses energy from radio-waves taht are applied with a small probe at several points in the periphery of the cornea to reshape the eye’s surface. A topographic map helps to create the image of the eye’s surface to customise the treatment plans.
- Corneal Transplant: Few people can’t tolerate the contact lenses or other therapies to get normal vision and in advanced cases corneal transplant is considered. In cases of severe keratoconus this might be the last resort.
- Eye glasses or soft contact lenses: It can be used to correct the mild nearsightedness and astigmatism caused due to keratoconus at an early stage.
What are the tests for diagnosis of Keratoconus?
- Slit lamp examination: An examination to check your eyes for any abnormalities.
- Keratometry: It is a diagnostic instrument to measure the curvature of the anterior segment of the cornea, particularly for assessing the extent and axis of astigmatism.
- Corneal Topography: It is a method for obtaining three dimensional mapping of the surface of your cornea.
- Corneal Pachymetry: It is a test to measure the thickness of cornea.