Key Takeaways
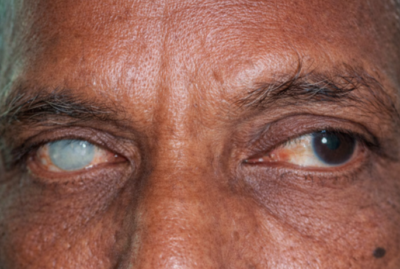
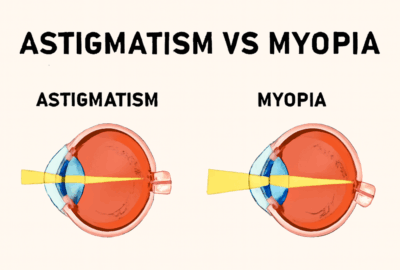
- Keratoconus thins the cornea and causes it to bulge into a conical shape, resulting in visual disturbances such as blurred and double vision.
- Keratoconus symptoms and signs include light sensitivity, eye fatigue, and perception of numerous or ghostly images.
- Corneal topography is a non-surgical imaging method that plots the corneal surface to diagnose keratoconus.
- A slit lamp examination employs light to evaluate the shape of the cornea and examine the eyes for disease.
- Computer-assisted keratometry and corneal mapping measure the shape and thickness of the cornea for diagnostic purposes.
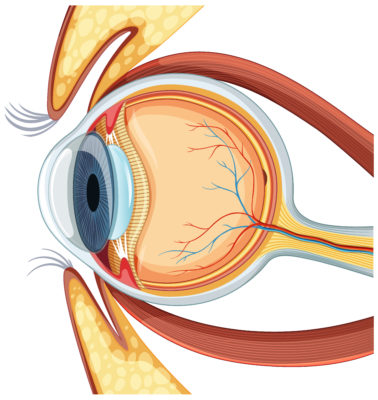
Keratoconus is a condition in which the normally round cornea (the transparent front part of an eye) becomes thin and develops a cone-like bulge.
What are the symptoms of Keratoconus?
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Light sensitivity
- Multiple images
- Eye strain
- ‘Ghost images’ – Appearance like several images when looking at one object
What do you mean by Corneal Topography?
Corneal Topography is also known as photokeratoscopy or videokeratography. Corneal Topography is an invasive medical imaging technique which is helpful for mapping the surface curvature of the cornea.
Corneal topography is helpful for the diagnosis of Keratoconus as it screens and analyses the diameter of the ring reflections and measures the radius of curvature at specific points and across the entire corneal surface.
What are the other tests for the diagnosis of Keratoconus?
- Slit lamp Examination:- In this test, a vertical beam light is focused on the surface of the eye. It helps to evaluate the shape of the cornea and eye diseases.
- Keratometry:- It is a test to measure the reflection and basic shape of the cornea.
- Computerised corneal mapping: – It is a special photographic test to record the images of the cornea and create a detailed map of the cornea’s surface. This test helps to measure the thickness of the cornea.