People today are increasingly interested in how lifestyle choices affect health. Patients with glaucoma want to help themselves and save their sight in any way they can in addition to the medications and surgery.
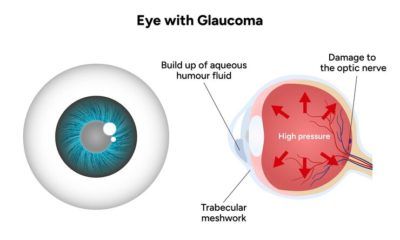
The traditional view has been that lifestyle choices do not play a role in glaucoma, but several studies show that lifestyle factors can influence eye pressure, which is a major risk factor for glaucoma. There is little data, however, on whether these factors impact the development (or worsening) of glaucoma.
For example, factors that increase eye pressure do not necessarily increase the risk of glaucoma and factors that lower eye pressure may not protect one from developing glaucoma. Sustained lowering of eye pressure is the most important part of glaucoma treatment, and lifestyle changes are only complementary.
Exercise: Aerobic exercise helps lower eye pressure, but the studies were not conducted in glaucoma patients and you must have approval from your primary physician first. Weightlifting can raise eye pressure, especially if the breath is held; but it is also a form of exercise and the effects of exercise are generally positive.
Yoga: Head-down positions can increase eye pressure and are not recommended for glaucoma patients. Certain types of activities, including pushups and lifting heavy weights, should be avoided by glaucoma patients.
Both normal and glaucoma study participants showed a rise in IOP in all four yoga positions, with the greatest increase of pressure occurring during downward facing position
High-resistance wind instruments: includes trumpet and oboe; eye pressure increases while playing these.
Marijuana: Smoking marijuana can lower eye pressure. However, due to its short duration of action (3-4 hours), side effects, and lack of evidence that it alters the course of glaucoma, it is not recommended for glaucoma treatment.
Alcohol: Lowers eye pressure for a short duration but some studies suggest that daily alcohol consumption is associated with higher eye pressure. Alcohol use does not appear to alter the risk of developing glaucoma.
Cigarettes: Studies indicate that smoking cigarettes increases the risk of glaucoma, and has an overall negative impact on eye health.
Caffeine: Drinking coffee increases eye pressure for a short duration. A little coffee is fine, but excessive caffeine intake is not ideal. One study found that drinking 5 or more cups of caffeinated coffee increased the risk of developing glaucoma.
In summary, lifestyle choices can modify eye pressure and may influence the risk of developing glaucoma. Since there is not enough clinical data to make broad recommendations regarding lifestyle factors; you should discuss with your glaucoma eye doctor whether specific changes may be appropriate for you.